Charting Outcomes™: COMLEX-USA Level 1 Exam Baseline
How to Interpret the Data
It is important to note that only applicants who indicated completion of the USMLE Step 1 or COMLEX-USA Level 1 exam prior to the transition to pass/fail (i.e., USMLE Step 1 exams taken after January 26, 2022 and COMLEX Level 1 exams taken after May 10, 2022) had the option to self-report their Step/Level 1 numeric score. In 2024, of applicants who participated in the Main Residency Match, 24.9% had Step 1 numeric scores available while only 2.0% had Level 1 numeric scores available.
The Charting Outcomes™: Characteristics of Applicants who Match to Their Preferred Specialty interactive reports consist of three components:
Component 1
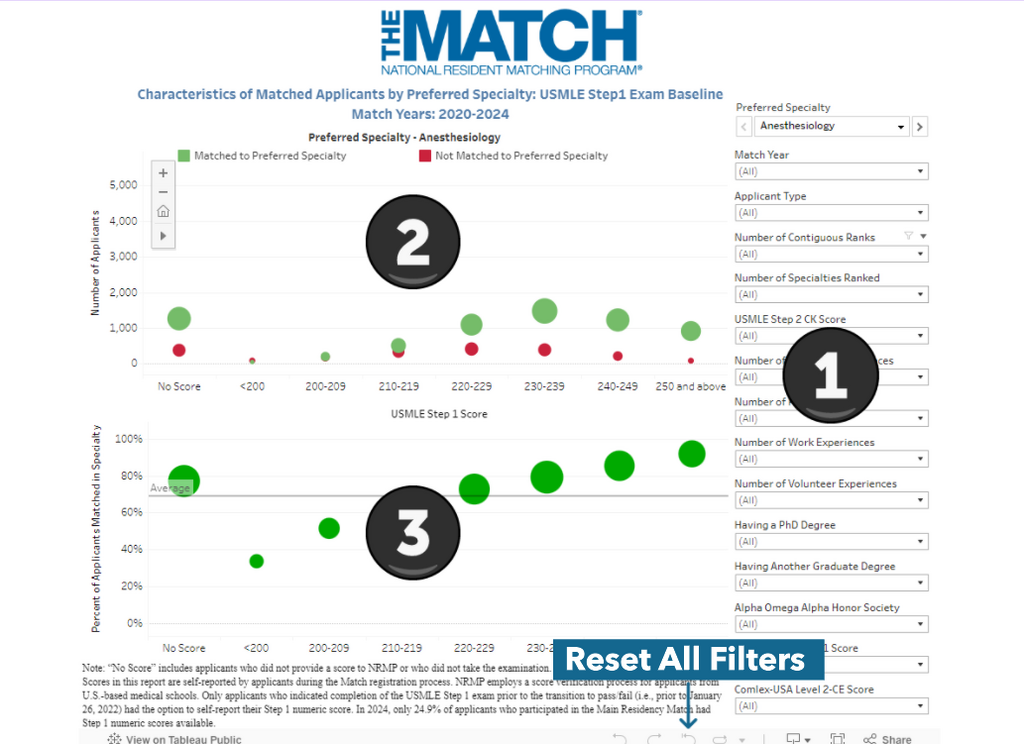
The right-hand column allows applicants to identify a specialty of interest, set the size of the database using a range of Match years, and enter personal characteristics using a variety of filters. Many of the filters allow for the selection of multiple options, so it is recommended that applicants include all options less than or equal to the intended value. For example, to filter the data based on 7 publications, check “no publications,” “less than 3,” “3-5,” and “5-10.” The “Reset Filters” button can be used at any time to clear the filters.
Component 2 and 3
The charts, present the data based on the numbers and percentages of applicants matched to the specialty (and it was their preferred specialty) by their United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 scores or their Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination of the United States (COMLEX-USA) Level 1 scores.
Top Chart (2)
The top chart shows the numbers of matched applicants in green and the numbers of unmatched applicants in red.
Bottom Chart (3)
The bottom chart computes the percentages of matched applicants using the numbers in Component 2.
The sizes of the dots in both charts reflect the magnitude of the data points. By hovering the mouse over any data point, the data point will be highlighted within the same USMLE Step 1 or COMLEX-USA Level 1 score range. The “tooltip” pop-up provides some basic information on the data point.
DEFINITIONS
Preferred Specialty
The specialty of the first program on the rank order list. An applicant does not have a preferred specialty when 1) a preliminary program is ranked first or 2) as part of a couple, the applicant selects “no match” as the first rank opposite the partner’s ranked program/specialty.
Matched/Not Matched to the Preferred Specialty
Whether or not an applicant matches to the specialty of the first program on their rank order list.
Number of Contiguous Ranks
The number of programs ranked in the first-choice (preferred) specialty before a program in another specialty appeared on an applicant’s rank order list.
Number of Abstracts/Presentations/Publications
The total number of all abstracts, presentations, and publications self-reported by NRMP registrants based on what they entered in their application.
Number of Research/Volunteer/Work Experiences
The total number of research/volunteer/work experiences reported self-reported by NRMP registrants based on what they entered in their application.
DATA CONSIDERATIONS
- Only specialties that offer 50 or more positions in the Main Residency Match are included.
- With the exception of applicant type, all applicant characteristics are self-reported. U.S. MD and DO medical schools have verified most USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores and COMLEX-USA Level 1 and Level 2-CE scores for U.S. MD and DO seniors and graduates. Other scores, primarily for students and graduates of international medical schools (IMGs) have not been verified.
- Due to the transition of medical licensure Step/Level 1 exams to pass/fail, in 2024, of applicants who participated in the Main Residency Match, 24.9% had Step 1 numeric scores available while only 2.0% had Level 1 numeric scores available.
- Not all applicants consented to provide or provided information; accordingly, missing data exist in all characteristics.
REMINDER
Data can become less representative and may not be helpful if the criteria are refined too narrowly and the sample size becomes very small.